Content
# dbt MCP Server
[](https://www.bestpractices.dev/projects/11137)
This MCP (Model Context Protocol) server provides various tools to interact with dbt. You can use this MCP server to provide AI agents with context of your project in dbt Core, dbt Fusion, and dbt Platform.
Read our documentation [here](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/dbt-ai/about-mcp) to learn more. [This](https://docs.getdbt.com/blog/introducing-dbt-mcp-server) blog post provides more details for what is possible with the dbt MCP server.
## Experimental MCP Bundle
We publish an experimental Model Context Protocol Bundle (`dbt-mcp.mcpb`) with each release so that MCPB-aware clients can import this server without additional setup. Download the bundle from the latest release assets and follow Anthropic's [`mcpb` CLI](https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/mcpb) docs to install or inspect it.
## Feedback
If you have comments or questions, create a GitHub Issue or join us in [the community Slack](https://www.getdbt.com/community/join-the-community) in the `#tools-dbt-mcp` channel.
## Architecture
The dbt MCP server architecture allows for your agent to connect to a variety of tools.
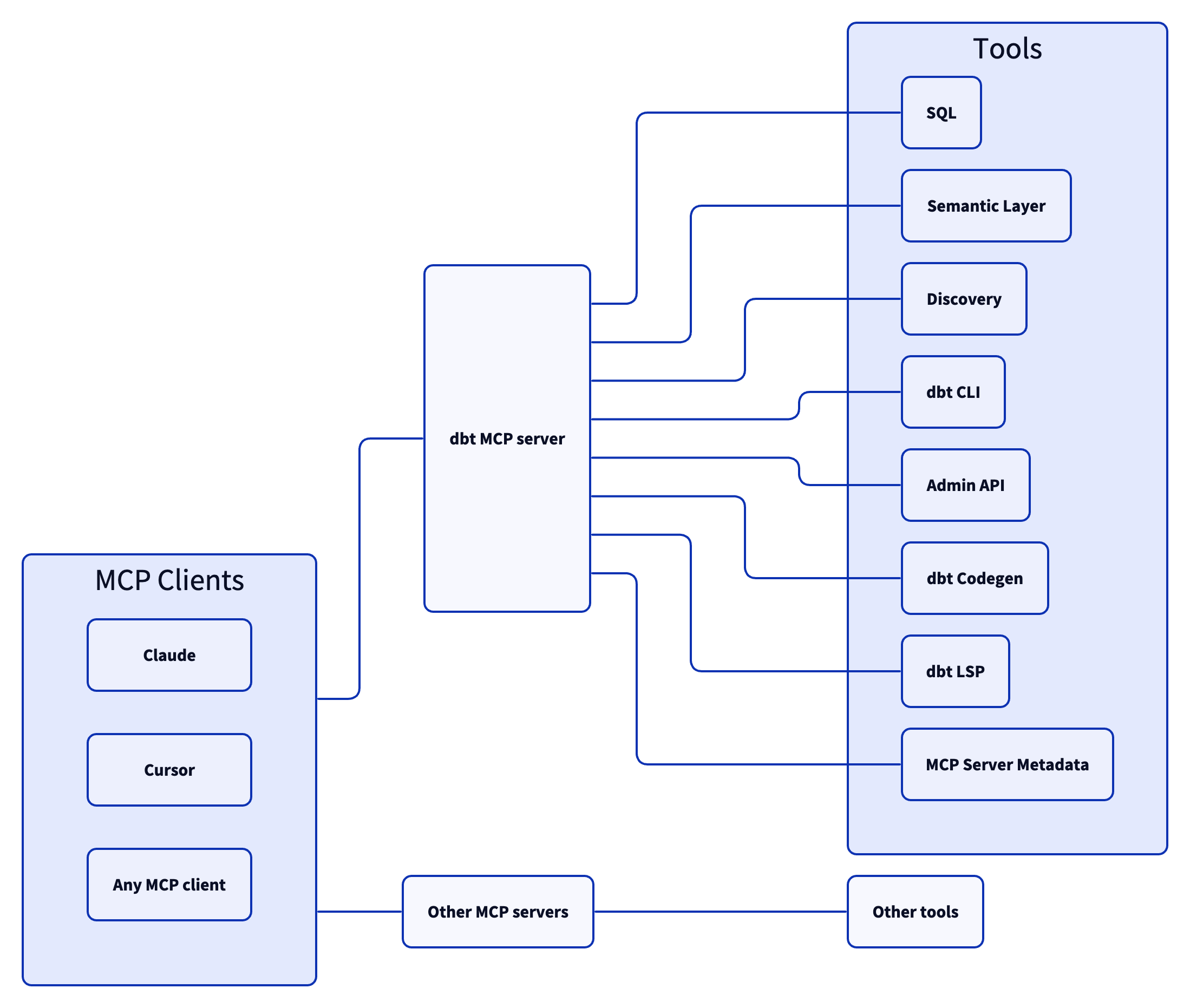
## Tools
### SQL
Tools for executing and generating SQL on dbt Platform infrastructure.
- `execute_sql`: Executes SQL on dbt Platform infrastructure with Semantic Layer support.
- `text_to_sql`: Generates SQL from natural language using project context.
### Semantic Layer
To learn more about the dbt Semantic Layer, click [here](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/use-dbt-semantic-layer/dbt-sl).
- `get_dimensions`: Gets dimensions for specified metrics.
- `get_entities`: Gets entities for specified metrics.
- `get_metrics_compiled_sql`: Returns compiled SQL for metrics without executing the query.
- `list_metrics`: Retrieves all defined metrics.
- `list_saved_queries`: Retrieves all saved queries.
- `query_metrics`: Executes metric queries with filtering and grouping options.
### Discovery
To learn more about the dbt Discovery API, click [here](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/dbt-cloud-apis/discovery-api).
- `get_all_macros`: Retrieves macros; option to filter by package or return package names only.
- `get_all_models`: Retrieves name and description of all models.
- `get_all_sources`: Gets all sources with freshness status; option to filter by source name.
- `get_exposure_details`: Gets exposure details including owner, parents, and freshness status.
- `get_exposures`: Gets all exposures (downstream dashboards, apps, or analyses).
- `get_lineage`: Gets full lineage graph (ancestors and descendants) with type and depth filtering.
- `get_macro_details`: Gets details for a specific macro.
- `get_mart_models`: Retrieves all mart models.
- `get_model_children`: Gets downstream dependents of a model.
- `get_model_details`: Gets model details including compiled SQL, columns, and schema.
- `get_model_health`: Gets health signals: run status, test results, and upstream source freshness.
- `get_model_parents`: Gets upstream dependencies of a model.
- `get_model_performance`: Gets execution history for a model; option to include test results.
- `get_related_models`: Finds similar models using semantic search.
- `get_seed_details`: Gets details for a specific seed.
- `get_semantic_model_details`: Gets details for a specific semantic model.
- `get_snapshot_details`: Gets details for a specific snapshot.
- `get_source_details`: Gets source details including columns and freshness.
- `get_test_details`: Gets details for a specific test.
- `search`: [Alpha] Searches for resources across the dbt project (not generally available).
### dbt CLI
Allowing your client to utilize dbt commands through the MCP tooling could modify your data models, sources, and warehouse objects. Proceed only if you trust the client and understand the potential impact.
- `build`: Executes models, tests, snapshots, and seeds in DAG order.
- `compile`: Generates executable SQL from models/tests/analyses; useful for validating Jinja logic.
- `docs`: Generates documentation for the dbt project.
- `get_lineage_dev`: Retrieves lineage from local manifest.json with type and depth filtering.
- `get_node_details_dev`: Retrieves node details from local manifest.json (models, seeds, snapshots, sources).
- `list`: Lists resources in the dbt project by type with selector support.
- `parse`: Parses and validates project files for syntax correctness.
- `run`: Executes models to materialize them in the database.
- `show`: Executes SQL against the database and returns results.
- `test`: Runs tests to validate data and model integrity.
### Admin API
To learn more about the dbt Administrative API, click [here](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/dbt-cloud-apis/admin-cloud-api).
- `cancel_job_run`: Cancels a running job.
- `get_job_details`: Gets job configuration including triggers, schedule, and dbt commands.
- `get_job_run_artifact`: Downloads a specific artifact file from a job run.
- `get_job_run_details`: Gets run details including status, timing, steps, and artifacts.
- `get_job_run_error`: Gets error and/or warning details for a job run; option to include or show warnings only.
- `get_project_details`: Gets project information for a specific dbt project.
- `list_job_run_artifacts`: Lists available artifacts from a job run.
- `list_jobs`: Lists jobs in a dbt Platform account; option to filter by project or environment.
- `list_jobs_runs`: Lists job runs; option to filter by job, status, or order by field.
- `list_projects`: Lists all projects in the dbt Platform account.
- `retry_job_run`: Retries a failed job run.
- `trigger_job_run`: Triggers a job run; option to override git branch, schema, or other settings.
### dbt Codegen
These tools help automate boilerplate code generation for dbt project files.
- `generate_model_yaml`: Generates model YAML with columns; option to inherit upstream descriptions.
- `generate_source`: Generates source YAML by introspecting database schemas; option to include columns.
- `generate_staging_model`: Generates staging model SQL from a source table.
### dbt LSP
A set of tools that leverage the Fusion engine for advanced SQL compilation and column-level lineage analysis.
- `fusion.compile_sql`: Compiles SQL in project context via dbt Platform.
- `fusion.get_column_lineage`: Traces column-level lineage via dbt Platform.
- `get_column_lineage`: Traces column-level lineage locally (requires dbt-lsp via dbt Labs VSCE).
### Product Docs
Tools for searching and fetching content from the official dbt documentation at docs.getdbt.com.
- `get_product_doc_pages`: Fetches the full Markdown content of one or more docs.getdbt.com pages by path or URL.
- `search_product_docs`: Searches docs.getdbt.com for pages matching a query; returns titles, URLs, and descriptions ranked by relevance. Use get_product_doc_pages to fetch full content.
### MCP Server Metadata
These tools provide information about the MCP server itself.
- `get_mcp_server_branch`: Returns the current git branch of the running dbt MCP server.
- `get_mcp_server_version`: Returns the current version of the dbt MCP server.
## Examples
Commonly, you will connect the dbt MCP server to an agent product like Claude or Cursor. However, if you are interested in creating your own agent, check out [the examples directory](https://github.com/dbt-labs/dbt-mcp/tree/main/examples) for how to get started.
## Dependencies
Dependencies are pinned to specific versions and are not updated automatically. Only security-related dependency updates are submitted via automated pull requests.
## Contributing
Read `CONTRIBUTING.md` for instructions on how to get involved!
Connection Info
You Might Also Like
markitdown
Python tool for converting files and office documents to Markdown.
markitdown
MarkItDown-MCP is a lightweight server for converting URIs to Markdown.

Filesystem
Node.js MCP Server for filesystem operations with dynamic access control.

Sequential Thinking
A structured MCP server for dynamic problem-solving and reflective thinking.

Fetch
Retrieve and process content from web pages by converting HTML into markdown format.
TrendRadar
TrendRadar: Your hotspot assistant for real news in just 30 seconds.